Explore the Fleet
Discover different rocket designs and their unique characteristics
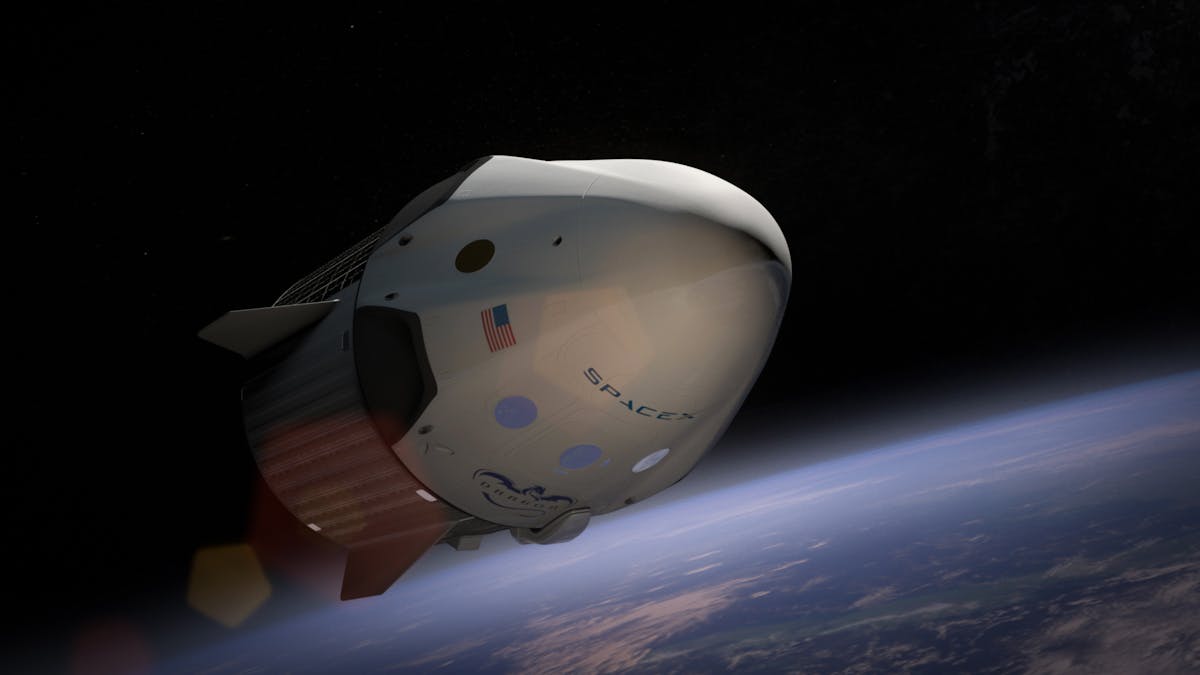

Space Shuttle Discovery
Final mission of Space Shuttle Discovery, delivering the Permanent Multipurpose Module to the ISS.

Space Shuttle Discovery
Feb 24, 2011
Falcon Heavy
Feb 6, 2018

Saturn V
Jul 16, 1969

Starship
Mar 14, 2024

Atlas V
Jul 30, 2020
Test Your Knowledge
Engage with interactive quizzes designed to reinforce key concepts
Multiple Choice
Fill the Blanks
Match Concepts
Sequence Builder
Arrange the launch sequence in correct order:
- First Stage: Main boosters
- Payload: Deploy satellite
- Third Stage: Final trajectory
- Second Stage: Orbital insertion
Key Concepts
Flip through essential rocket science principles
Click any card to reveal the answer
Physics Playground
Experiment with rocket parameters and see real-time calculations
Thrust Equation
F = ṁVₑ + (Pₑ - Pₐ)Aₑ
Momentum thrust dominates — typical for high-altitude operation
Tsiolkovsky Rocket Equation
Δv = vₑ ln(m₀/mf)
Low mass ratio — limited delta-v capability.
Rocket Comparison
Compare different rocket types and understand their trade-offs
See It In Action
Watch a detailed explanation of rocket mechanics
FAQ
Quick answers to frequently asked questions
Ready to Launch?
Continue your journey through space exploration